Liquidity, currency
The euro gained while the dollar lost ground
The signs of weakness in the US economy were immediately acknowledged with a weaker dollar. The US Federal Reserve sees a risk of stagflation in the US due to the drastic tariff increases, rapidly increasing political uncertainty and deteriorating consumer sentiment. The euro, on the other hand, gained in value as the “United States of Europe” is willing to do more for its security and defense.
Read more Close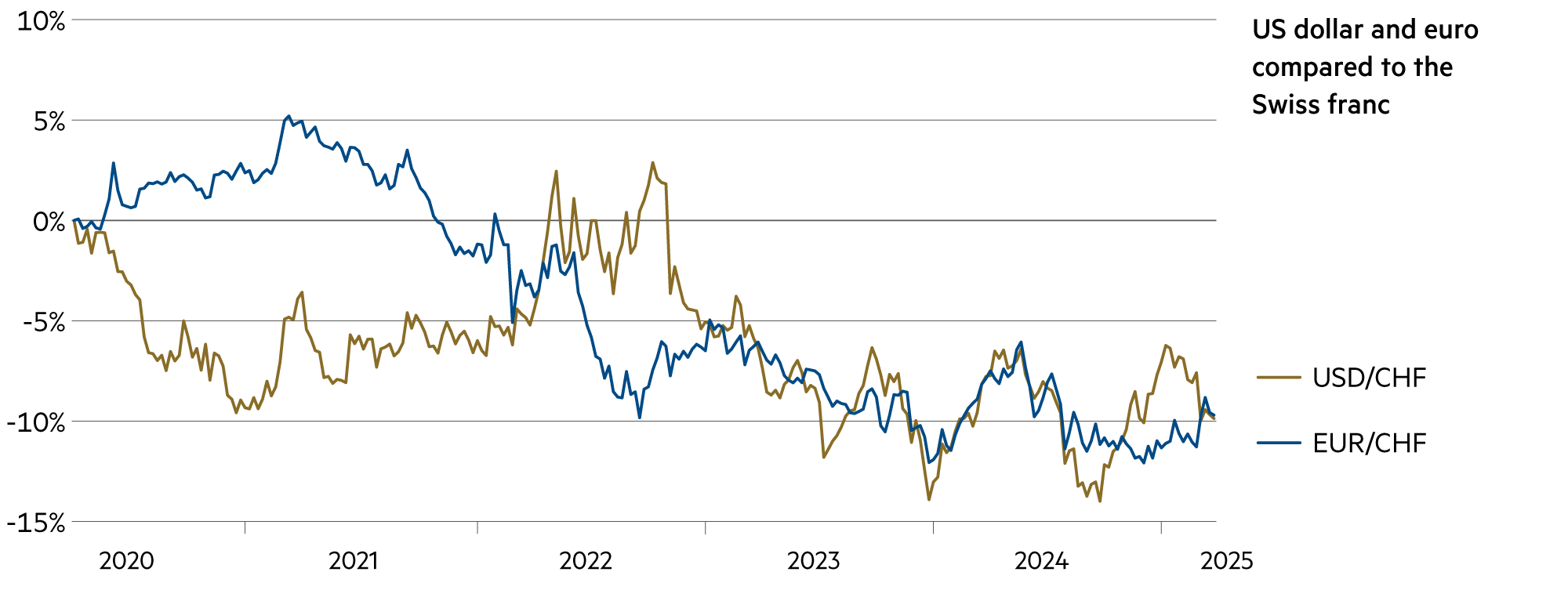
But over five years, one thing is clear: both currencies (euro and dollar) are on a downward trend against the Swiss franc. The euro lost 9.8% during this period, the dollar 8%. According to purchasing power parity, however, the dollar is under greater downward pressure.
Consumer sentiment in the US is also being cited as a sign of weakness. It has plummeted under the influence of erratic tariff policy, when long-term inflation expectations (3.9%) reached their highest level in 32 years. This underscored fears that Donald Trump’s economic policy is weighing on the economy.
The University of Michigan’s sentiment index fell to 57.9 in March. This is the third consecutive monthly decline and significantly lower than economists had expected. Retail sales did at least pick up slightly in February (+0.2%) after falling sharply in January (-1.2%). In the US, the wealth effect plays a central role because 90% of savings are invested in equities. If US equity prices fall, this has an immediate impact on consumer sentiment – not only among low-income households, but also among high-income and wealthy households. Finally, consumer behavior in restaurants and bars is closely monitored. Here, there was the sharpest decline in a year.
After the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) cut interest rates by a total of 100 basis points in the last three monetary policy meetings of 2024, it voted in January to leave the target range for the federal funds rate at 4.25% to 4.50% and confirmed this in March. There is no significant change in the forward guidance on key rates in the updated Fed statement.
However, the FOMC’s economic forecasts are pessimistic. The median forecast for GDP growth in 2025 fell from 2.1% to 1.7%, with a range of 1.5% to 1.9%. The median forecast for the unemployment rate at the end of 2025 rose from 4.3% to 4.4%, and that for core PCE inflation rose from 2.5% to 2.8%. The range for core inflation has widened in view of the many uncertainties and is 2.5% to 3.5% for the current year.
This means that the probability of an economic downturn is greater than that of an upward movement. It remains unclear where the downward trend will end. In any case, the probability of a recession increased to 27% according to the Fed in New York. The Fed’s forecast unit in New York currently sees an unchanged high, significant increase (+2.9%) in the real-time GDP estimate. By contrast, the Fed in Atlanta currently sees a significant decline (-2.8%).
| Asset class | 3–6 months | 12–24 months | Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bank account |
|
|
At the short end, banks are lending to each other at just 0.18% (3 months), 0.16% (6 months) and 0.12% (12 months). The scope for interest rates is narrowing. |
| Euro / Swiss franc |
|
|
The ECB is highly likely to move to the next interest rate hike on April 17, which would take the target rate to 2.25%. |
| US dollar / Swiss franc |
|
|
The Fed fund rates will remain unchanged at a high level until June 18, and will continue to be restrictive, forcing the economy to cool down. |
| Euro / US dollar |
|
|
The exchange rate could rise from the current 1.08 to 1.15-1.18 within twelve months if the European economy continues to accelerate. |