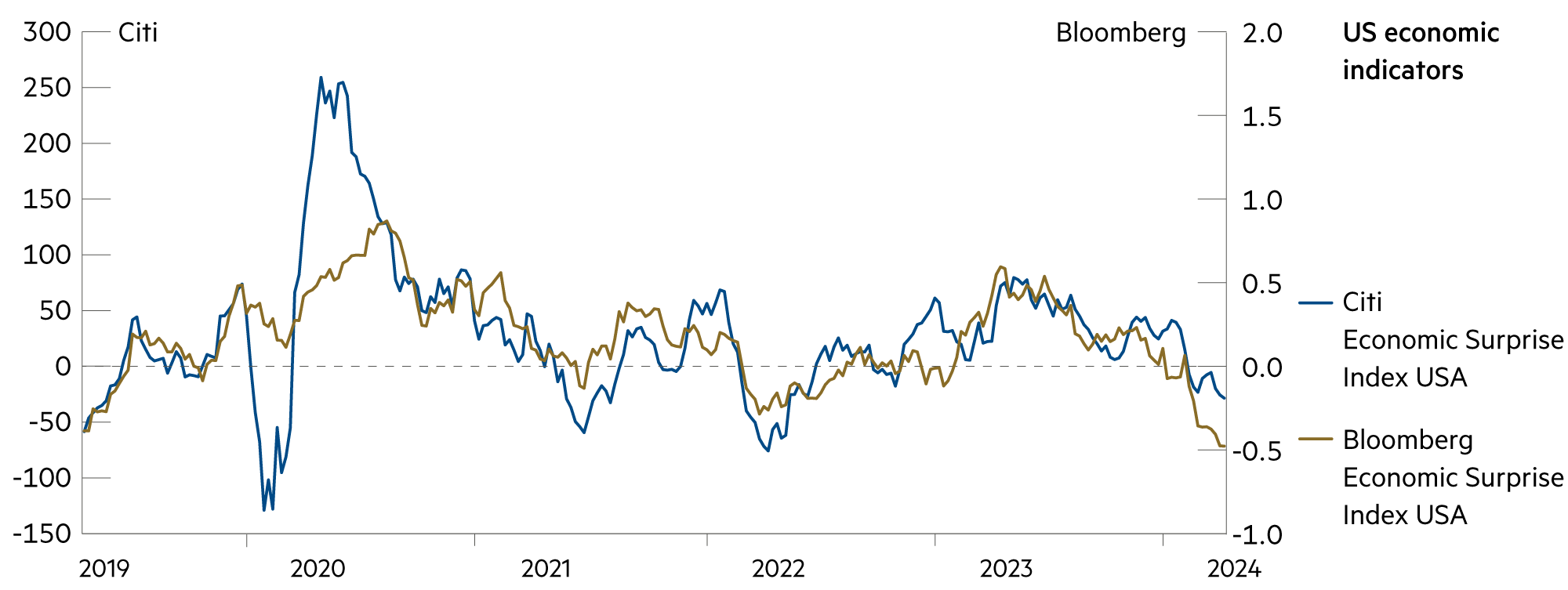Liquidity, currency
Rate forecasts convey confidence
The interest rate forecasts of the various central banks convey the confidence that inflation rates in the most important currency areas will increasingly settle in the range between 1% and 3%. It is therefore to be expected that several central banks will begin to ease their restrictive monetary policy with cautious steps in the third quarter.
Read more Close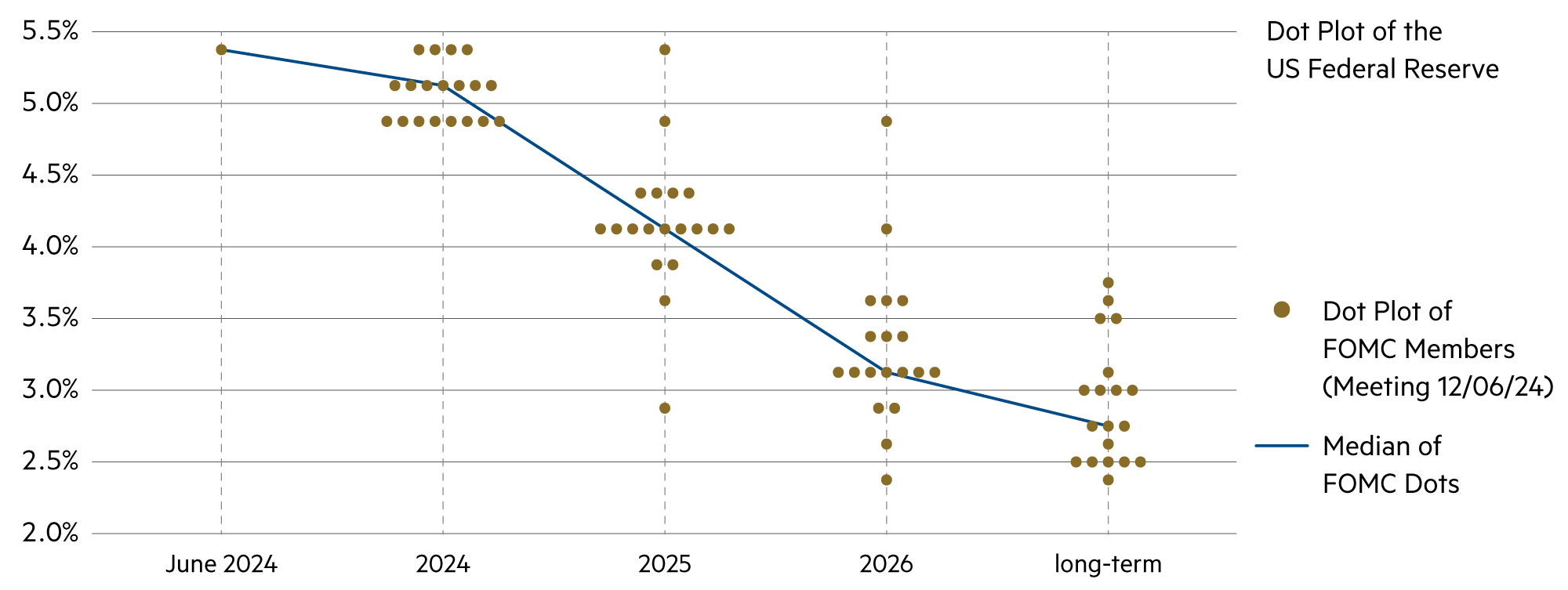
No monetary policy news is expected in the coming weeks. The summer break is coming to the fore, as is the half-yearly analysis, before the corresponding measures are taken in late summer. Monetary easing can be expected for the time being. Construction in particular, but also industry and service providers, grew in the first quarter of 2024, albeit at a slower pace. In construction, higher financing costs in the US, the eurozone and the UK are weighing heavily on investment. Consumers are also increasingly reluctant to spend. At the same time, there are also encouraging signs. Lower inflation rates and strong wage growth with a still robust labor market could encourage private households to consume more. And companies’ business expectations have recently improved significantly. Overall, the economy should gradually pick up speed without immediately driving up inflation again.
The economy in the eurozone is developing remarkably robustly. The forecasts for 2025 are positive and the unemployment rate is at an all-time low. From a monetary policy perspective, it is important that inflation, which is still too high, falls back to its target value of 2%. According to the flash estimate, the inflation rate in the eurozone was 2.6% in May. This is slightly higher than in April, but significantly lower than in fall 2022, when inflation in the eurozone was still around 11%. However, the return to the target value of 2% is not a foregone conclusion. According to the flash estimate, service prices rose by 4.1% in May compared to the same month last year, while goods prices reached the target value.
However, the interest rate shock, which is still reflected in the valuation of bonds in particular, was severe. Starting in July 2022, the European Central Bank (ECB) raised interest rates ten times in a row and then left them at this high level for nine months from September 2023. And now the ECB has lowered the interest rate for the deposit facility, which is currently decisive for monetary policy, from 4.0% to 3.75%.
There are likely to be two more cuts by the end of this year, perhaps three, but we remain cautious. This is because there is still considerable uncertainty about future economic and price developments. Metaphorically speaking: The ECB does not see itself on a mountaintop from which it will inevitably descend. Rather, it sees itself on a ridge where the right point for the further descent still needs to be found. The Governing Council of the ECB recently emphasized that decisions are data-dependent and made on a meeting-by-meeting basis.
| Asset class | 3–6 months | 12–24 months | Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bank account |
|
|
The SNB's key interest rate cut on June 25 also caused interest rates on bank deposits and money market investments to fall. They are below inflation (1.3%). |
| Euro / Swiss franc |
|
|
The ECB's future interest rate path is likely to be "gradual" in nature, i.e. at a pace of quarterly steps rather than from meeting to meeting. |
| US dollar / Swiss franc |
|
|
At 0.90, the dollar is at a high level due to interest rates. The annualized hedging costs of 4.3% against the franc are correspondingly high. |
| Euro / US dollar |
|
|
At 1.07, the euro has remained fairly steady against the dollar since its inception. No radical changes are to be expected, but a slight improvement of the Euro. |