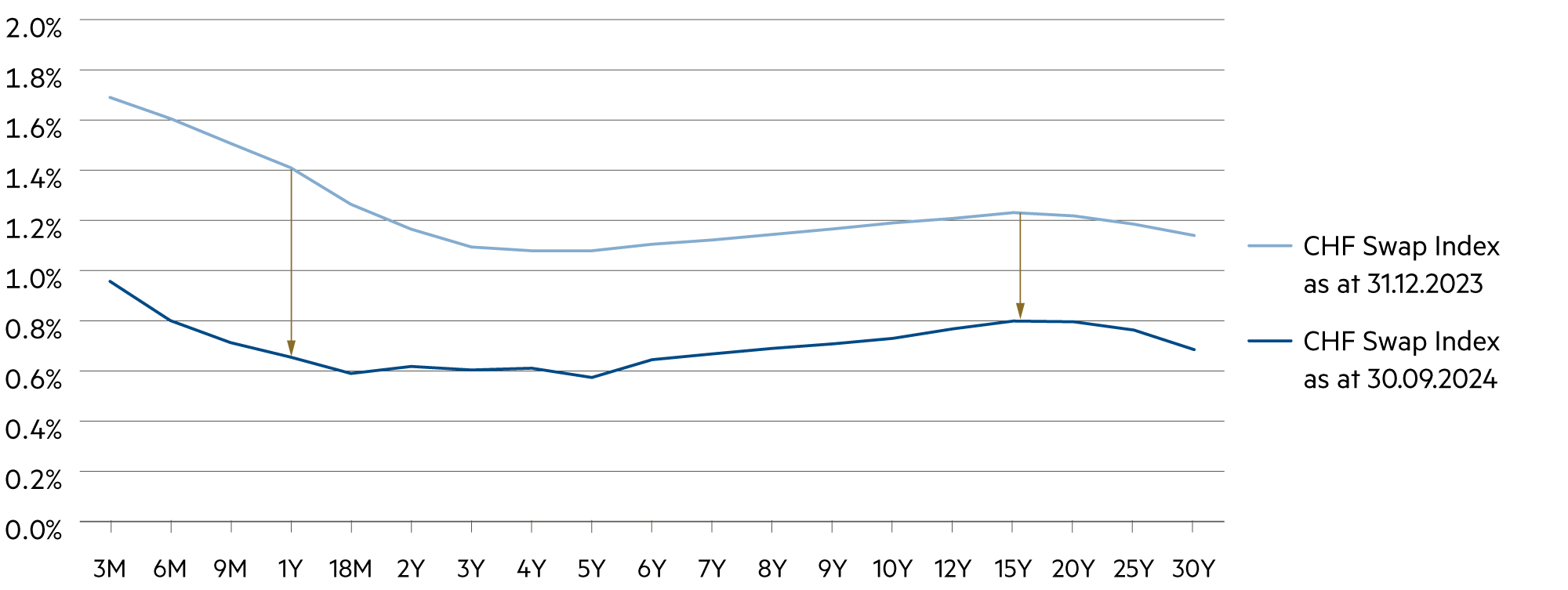
Liquidity, currency
Inflation is under control
In Switzerland, inflation fell to 0.8% in September. In the eurozone, it fell to 1.8%. Using the same measurement method, it is also below the target level of 2% in the USA. The residual inflation that exists is currently being driven by services in many areas. The observed decline in inflation – from over 10% to below 2% in the eurozone, for example – is generally more pronounced than central banks had anticipated. As a result, various central banks will cut their key rates further in the fourth quarter.
Read more Close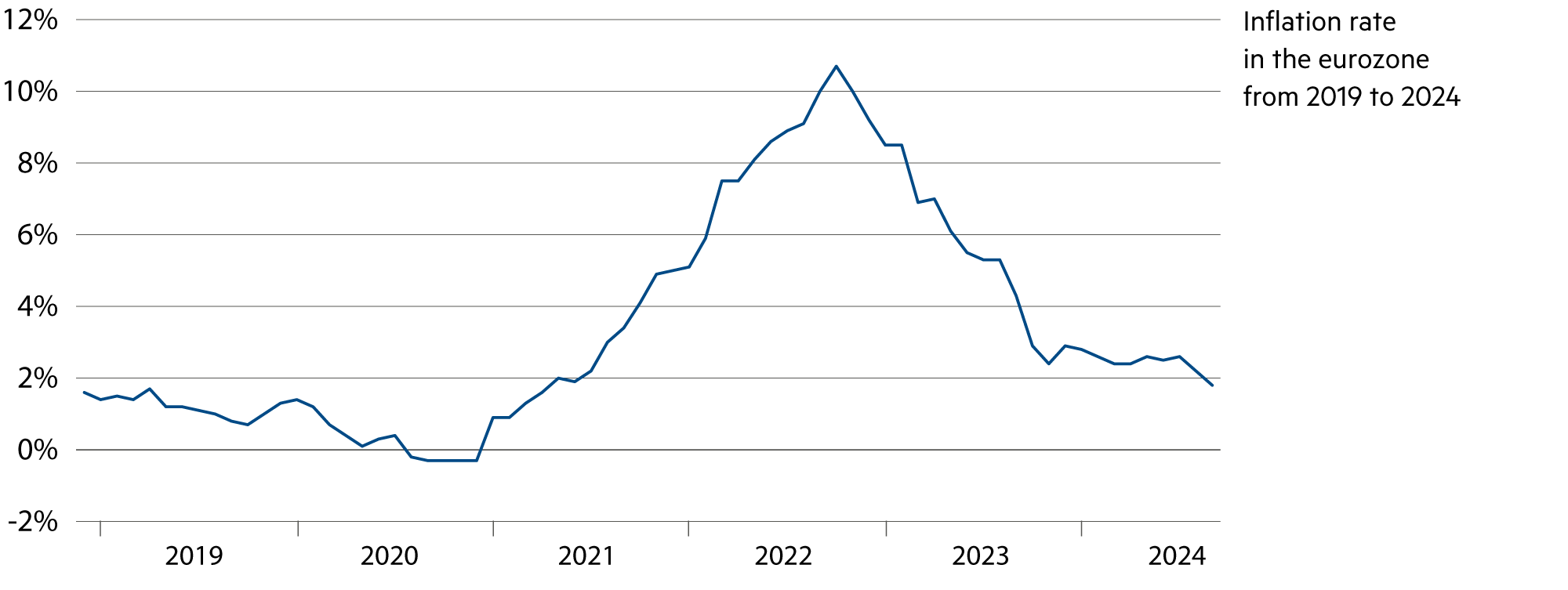
The SNB’s new conditional inflation forecast is well below the level projected at the monetary policy assessment in June. The stronger Swiss franc, lower oil price and the cuts in electricity prices announced for next January contributed to the downward revision. With the sharper fall in inflation, the SNB also expects lower second-round effects in the medium term. The new forecast is 0.6% for 2025 and 0.7% for 2026 on an annual average. If interest rates had not been cut, the inflation forecasts would be even lower.
A similar picture can be seen for inflation in the eurozone, which fell to 1.8% in September. The last time inflation was below the 2% mark was in May 2021. The data increased the probability on the financial markets that the ECB would lower key interest rates further at its next interest rate meeting on October 17, rather than waiting until December.
Shortly thereafter, on November 5, Americans will be able to choose between Democrat Kamala Harris and Republican Donald Trump in the presidential election. According to today’s media reports, the outcome will probably also influence the Fed’s monetary policy. Observers assume that an election victory for Trump could end the Fed’s cycle of interest rate cuts as early as the second quarter of 2025, as the Republicans’ economic program would favor higher inflation.
If Harris wins the election, economists believe we could see regular rate cuts to around 3% by mid-2025. Harris had also insisted that she would not interfere with the Fed’s work as president, while Trump had indicated that he would try to influence the Fed’s monetary policy if re-elected. This is unconstitutional, but it does not bother him at all.
Meanwhile, US Fed Chairman Jerome Powell reaffirmed his confidence that inflation will continue to move towards the target of two percent. According to the harmonized method of measuring inflation, as primarily used by European countries, inflation in the US is 1.9%. “If the economy develops as expected, interest rate policy will move towards a more neutral stance over time,” Powell said recently at a financial conference in Nashville, Tennessee. However, the Fed is not pursuing a fixed course. With a target range of 4.75% to 5.0%, the Fed is still pursuing a highly restrictive monetary policy. According to the latest assessment by Fed members, the neutral level is around 175 basis points lower at around 3.0%.
| Asset class | 3–6 months | 12–24 months | Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bank account |
|
|
Interest on time deposits is falling sharply and is trending towards 0.5%. With a few exceptions, savings accounts are paying even less interest. |
| Euro / Swiss franc |
|
|
The ECB is likely to lower its key rates again slightly in October. This should further reduce hedging costs (end of September: 2.5%). |
| US dollar / Swiss franc |
|
|
We expect the dollar to weaken further. From its end-April 2024 level of 0.92, the currency lost 8.0% to 0.85. |
| Euro / US dollar |
|
|
At 1.11, the euro remains slightly above the average range of the past nine months. |